| Revision as of 11:14, 17 August 2016 ddgonzal (Talk | contribs) (->Overview) <- Previous diff |
Revision as of 00:05, 13 March 2019 ddgonzal (Talk | contribs) Next diff -> |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| = Overview = | = Overview = | ||
| - | High compression can make your engine prone to pre-detonation (pinging) which can destroy the engine. A high-quench design can make more compression without pinging. | + | {{search|internal+combustion+quench|internal combustion quench}} |
| + | |||
| + | High compression can make your engine prone to pre-detonation (pinging) which can destroy the engine. A high-quench design can use more compression without pinging. Quench is also known as squish/quish/skish/squench. | ||
| To achieve quench: | To achieve quench: | ||
| - | * Fit flat-top pistons (e.g. stock KB10 coupe pistons fit the A12) | + | * Fit flat-top [[piston]]s (e.g. stock KB10 coupe pistons fit the A12) |
| * Select a closed combustion chamber head (e.g. early A12, or H89 or GX head) | * Select a closed combustion chamber head (e.g. early A12, or H89 or GX head) | ||
| * Use a thin head gasket, like the GX gasket | * Use a thin head gasket, like the GX gasket | ||
| Quench is likely responsible for 2% power increase, which is a similar to the increase from going from 9:1 to 10:1 compression alone. Adding compression with quench (a la the GX engine) is about a 4% power increase (the other 12% of the GX power increase comes from the higher revs/freer flowing induction). | Quench is likely responsible for 2% power increase, which is a similar to the increase from going from 9:1 to 10:1 compression alone. Adding compression with quench (a la the GX engine) is about a 4% power increase (the other 12% of the GX power increase comes from the higher revs/freer flowing induction). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote>[https://www.crankshaftcoalition.com/wiki/Quench#Piston_design Crankshaft Coalition]: For a wedge shaped combustion chamber like used in many engines, a flat top piston is the best design for promoting the quench</blockquote> | ||
| = Details = | = Details = | ||
| Line 16: | Line 20: | ||
| Wedge head (closed chamber, inline valves) | Wedge head (closed chamber, inline valves) | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=18153 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/thumbs/18153.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|18153}} |
| However in 1977 Datsun came out with a dished-piston design with high quench. | However in 1977 Datsun came out with a dished-piston design with high quench. | ||
| Wedge chamber (left) vs Open Chamber (right) | Wedge chamber (left) vs Open Chamber (right) | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=19795 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/photos/19795.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|19795}} |
| In 1981, they used an offset dish, so the dish does not interfere with the quench area. | In 1981, they used an offset dish, so the dish does not interfere with the quench area. | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=19796 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/photos/19796.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|19796}} |
| 1981-1982 H95 chambers | 1981-1982 H95 chambers | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=18154 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/photos/18154.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|18154}} |
| <br>More quench pad area than H89 head. Chambers are deep-pocket for high-swirl, with shorter valves than other A-series heads. | <br>More quench pad area than H89 head. Chambers are deep-pocket for high-swirl, with shorter valves than other A-series heads. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 40: | ||
| Measuring clearance | Measuring clearance | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=18156 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/thumbs/18156.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|18156}} |
| <br>In this example, block had been decked so that piston protrudes 0.006 inch above block. Felpro head gasket is 0.041 inch compressed, so quench clearance is 0.035 inch. | <br>In this example, block had been decked so that piston protrudes 0.006 inch above block. Felpro head gasket is 0.041 inch compressed, so quench clearance is 0.035 inch. | ||
| = Discussion = | = Discussion = | ||
| - | David Vizard -- the BMC A-series wizard -- [http://www.enginebuildermag.com/Article/2266/surfacing_equipment_can_increase_horsepower.aspx tells a story] of a 528 HP blown SBC V8 that was 8.5:1 on pump gas (retail petrol). By adding quench -- reducing block to head clearance to 0.75 mm -- the compression ratio went up to 9.1:1 and now was able to use 2 psi MORE boost for a total of 580 HP. Quench works. | + | David Vizard -- the BMC A-series wizard -- {{web|www.enginebuildermag.com/Article/2266/surfacing_equipment_can_increase_horsepower.aspx|tells a story}} of a 528 HP blown SBC V8 that was 8.5:1 on pump gas (retail petrol). By adding quench -- reducing block to head clearance to 0.75 mm -- the compression ratio went up to 9.1:1 and now was able to use 2 psi MORE boost for a total of 580 HP. Quench works. |
| Each .010 inch reduction in quench clearance was worth nearly 2% HP along with a 0.23 increase in compression. The HP increase came about 40% from the quench and 60% from the compression ratio increase. But more importantly, the CR increase did not result in earlier detonation when the quench increased. | Each .010 inch reduction in quench clearance was worth nearly 2% HP along with a 0.23 increase in compression. The HP increase came about 40% from the quench and 60% from the compression ratio increase. But more importantly, the CR increase did not result in earlier detonation when the quench increased. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 69: | ||
| <br>http://www.theoldone.com/articles/badtothebone/</blockquote> | <br>http://www.theoldone.com/articles/badtothebone/</blockquote> | ||
| - | Quech/squish/quish/skish is the key. Too much clearance and you get no effect. Too little clearance and at high RPMs the piston rock a bit and will hit the head. | + | Quench is the key. Too much clearance and you get no effect. Too little clearance and at high RPMs the piston rock a bit and will hit the head. |
| Maximum clearance to obtain a quench effect may be 0.060 inch. | Maximum clearance to obtain a quench effect may be 0.060 inch. | ||
| Line 73: | Line 77: | ||
| Nismo metal head gasket which is only 0.020 inch thick (0.50 mm) | Nismo metal head gasket which is only 0.020 inch thick (0.50 mm) | ||
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=23638 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/thumbs/23638.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|23638}} |
| - | 3 layers are rivited together | + | 3 layers are riveted together |
| - | <br>[http://datsun1200.com/modules/myalbum/photo.php?lid=23639 http://datsun1200.com/uploads/thumbs/23639.jpg] | + | <br>{{Album|23639}} |
| - | [[Category:Engine Mechanical]] | + | [[Category:Engine Mechanical]] {{End}} |
Revision as of 00:05, 13 March 2019
Proper quench in the combustion chamber results in more power, and more efficiency so higher fuel economy. It is less like to pre-detonate and will use less spark advance for the same power. It's a win-win scenerio. Datsun used it in some of the A-series engines.
Contents |
Overview
High compression can make your engine prone to pre-detonation (pinging) which can destroy the engine. A high-quench design can use more compression without pinging. Quench is also known as squish/quish/skish/squench.
To achieve quench:
- Fit flat-top pistons (e.g. stock KB10 coupe pistons fit the A12)
- Select a closed combustion chamber head (e.g. early A12, or H89 or GX head)
- Use a thin head gasket, like the GX gasket
Quench is likely responsible for 2% power increase, which is a similar to the increase from going from 9:1 to 10:1 compression alone. Adding compression with quench (a la the GX engine) is about a 4% power increase (the other 12% of the GX power increase comes from the higher revs/freer flowing induction).
Crankshaft Coalition: For a wedge shaped combustion chamber like used in many engines, a flat top piston is the best design for promoting the quench
Details
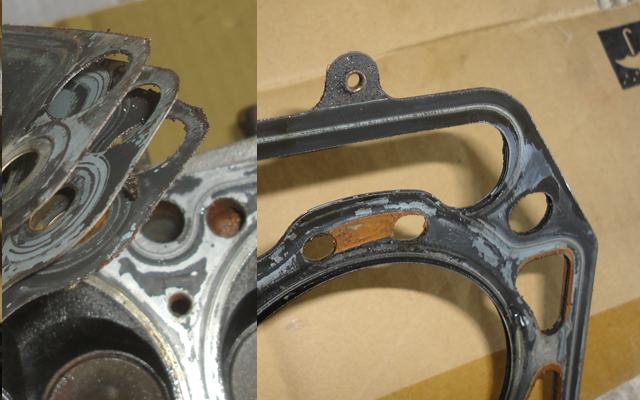
Quench traditionally is gained by using closed-chamber wedge heads with flat-top piston.
Wedge head (closed chamber, inline valves)

However in 1977 Datsun came out with a dished-piston design with high quench.
Wedge chamber (left) vs Open Chamber (right)
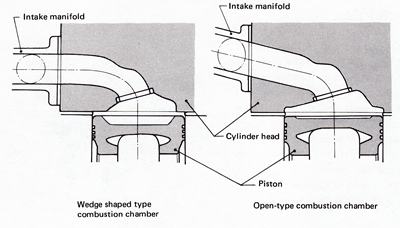
In 1981, they used an offset dish, so the dish does not interfere with the quench area.
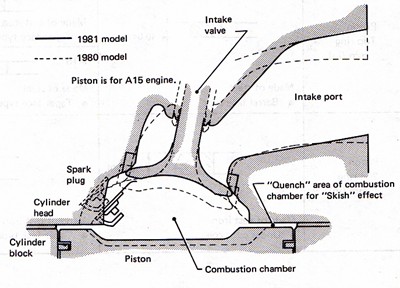
1981-1982 H95 chambers

More quench pad area than H89 head. Chambers are deep-pocket for high-swirl, with shorter valves than other A-series heads.
They say Small Block Chevy gains 1% HP for every 0.01" (0.25 mm) tighter quench (with same CR), and needs less spark advance, so less apt to ping.
Quench Clearance
If you use too thick gasket you lose the quench effect. The quench needs to be 0.75 to 0.50 mm to be effective from what I understand. Of course if you are using dished pistons there's no telling if it will have a proper quench effect.
Measuring clearance

In this example, block had been decked so that piston protrudes 0.006 inch above block. Felpro head gasket is 0.041 inch compressed, so quench clearance is 0.035 inch.
Discussion
David Vizard -- the BMC A-series wizard -- tells a story☁ of a 528 HP blown SBC V8 that was 8.5:1 on pump gas (retail petrol). By adding quench -- reducing block to head clearance to 0.75 mm -- the compression ratio went up to 9.1:1 and now was able to use 2 psi MORE boost for a total of 580 HP. Quench works.
Each .010 inch reduction in quench clearance was worth nearly 2% HP along with a 0.23 increase in compression. The HP increase came about 40% from the quench and 60% from the compression ratio increase. But more importantly, the CR increase did not result in earlier detonation when the quench increased.
Note that the datsun A-series "H89" head has similar combustion chambers to the SBC V8 engine (wedge head).
0.035 piston-to-head clearance with tight piston-to-bore clearance can be had with SBC, although 0.040 or 0.050 is safer with less precise engines. Stock SBC often has a 0.060 clearance. A small bore import engine *might* be safe at 0.030 (0.75 mm) clearance. Maybe even 0.025 would be OK.
Wiseco:
What is minimum piston to head clearance? A. ...Most imports can get by with as little as .030
never add a shim or head gasket to lower compression on a quench head engine. If you have 10:1 with a proper quench and then [use a thicker] .040" gasket to give 9.5:1 and .080" quench, you will create more ping at 9.5:1 than you had at 10:1.
http://racingarticles.com/article_racing-10.html
The [Honda B20] quench distance, or piston to head clearance had been set at .032”, to effectively give us “zero” quench clearance at 9500 rpm, due to rod stretch. .032” caused the pistons to hammer the head pretty hard at 10,000+
http://www.theoldone.com/articles/badtothebone/
Quench is the key. Too much clearance and you get no effect. Too little clearance and at high RPMs the piston rock a bit and will hit the head.
Maximum clearance to obtain a quench effect may be 0.060 inch.
Gaskets
Most A-series head gasket are 1.6 mm thick. Some are 1.2 mm thick.
Nismo metal head gasket which is only 0.020 inch thick (0.50 mm)


![[Datsun 1200 encyclopedia]](/wiki/upload/wiki.png)
