To totally modernize your engine, you may install a crank-trigger signaling sensor system. Crank Trigger is used for 1) EFI or for 2) a distributorless ignition system.
Contents |
Spark Control
An electronic ignition system (spark control) can work with all modern ECU, or with a standalone spark controller like MegaJolt. This allows for full spark mapping for a near-perfect spark curve. And because the geared distributor isn't used, the timing signal is more stable.
Two main methods of crank trigger ignition system:
ECU of modern vintage e.g. MegaSquirt EDIS controller e.g. MegaJolt or MegaSquirt
Note that the 1970s/1980s Datsun ECUs don't have spark-control capability, while MegaSquirt, recent Haltech, Wolf and most other populars ECUs do. They can also be run in spark-only mode for use with Carburetors (no EFI is needed).
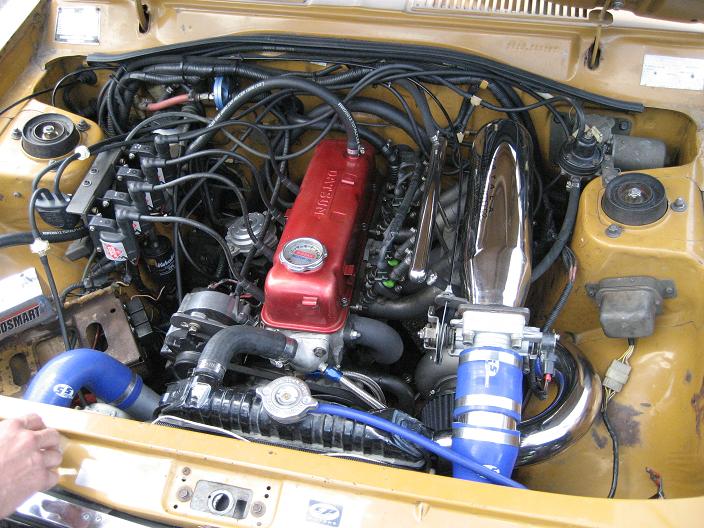
4-coils used with Crank Trigger
 album
album
EFI
Along with your Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) system, you can use the stock A12 distributor as an RPM signal. However, to totally modernize your engine, use a distributorless crank-trigger. The Crank Sensor (crank trigger) can do it.
Crank Trigger Types
Modern ECUs can read many kinds of crank trigger wheels such as the popular GM 72-2 wheels and the common Ford 36-1 wheels.
Missing-tooth wheel
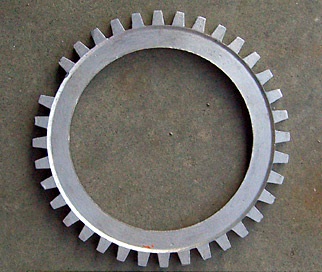
EDIS spark control systems only work with 36-1 wheels. This is a toothed metal wheel with 36 teeth, one of which is missing (and which pinpoints TDC).
A magnetic sensor of the Variable Reluctance type (VR Sensor) detects the spinning teeth an generates a signal. It is similar to a Hall Effect sensor, except those are more expensive, being a VR Sensor with a built in signal amplifier. Generally a Hall Effect sensor is not needed as modern controllers have built-in amplifiers and so can accept the raw signal.
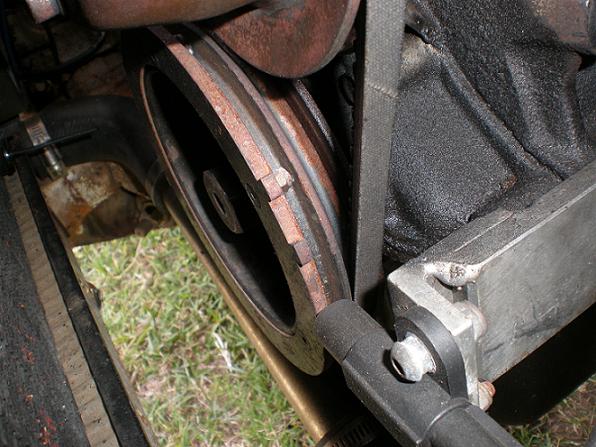
Alternatively, Trigger Teeth can be machined into an engine pulley, like on this CA18
 album
album
A crank trigger is usually taken from the front of the engine, but can also be taken from the rear of the crank, usually in the form of teeth machined into the flywheel.
Crank Trigger wheel machined into flywheel

(factory Ford piece shown)
Crank Trigger wheel at front of Datsun A12 crankshaft pulley
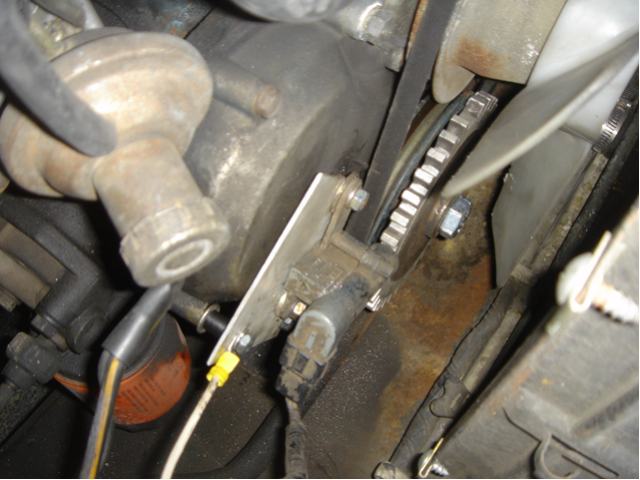 A-series 36-1 Kit
A-series 36-1 Kit
typical 2-wire VR sensor

V8 stamped-metal wheel (can be used on 4 cylinder engines)

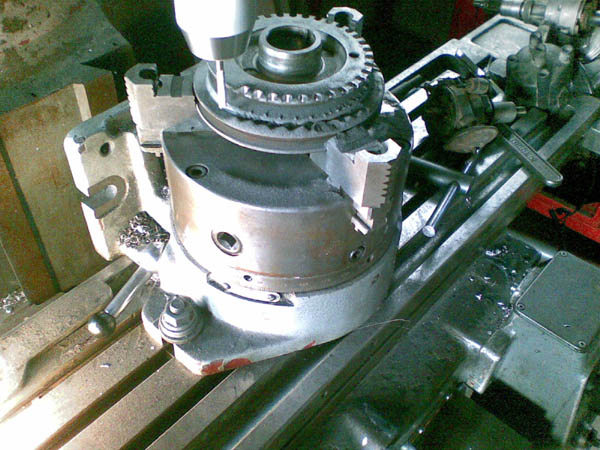
36-1 teeth being milled into a stock Datsun crank pulley:
 album
album
Crank Trigger Vs Cam Trigger
Crank Trigger tells the electronic controller where the crank is, so it can time the spark and get an RPM signal for the EFI brain. However, crank trigger does not indicate where exactly the engine is in the 4-stroke cycle. But thankfully that isn't needed to do EFI or spark control.
So what's a cam trigger for? Camshaft Position Sensor (CPS), also known as Cam Angle Sensor (CAS), is used to let the electronics know which cycle the engine is on. This is used for Sequential EFI or for sequential spark.
- Sequential EFI is EFI tuned to the specific cylinder. This reduces emissions and can slightly increase fuel economy slightly. Contrary to popular opinion, SEFI doesn't make any more power the regular EFI.
- Sequential spark is required for Coil-On-Plug ignition. See COP. Other than this, fully mapped spark only requires a crank sensor, via wasted spark (duplicated spark), as used by most engines since 1990. The famous GM twin-coil packs are wasted spark.
To get a CAS signal, the sensor must be driven off the cam, such as:
* Nissan Optical CAS works via the distributor * Have a sensor driven directly by the cam
There are no off-the-shelf cam-driven sensors for Datsun A-engine. But for example, the Nissan CA18DE engine uses a CAS on the left cam (front of engine).

![[Datsun 1200 encyclopedia]](/wiki/upload/wiki.png)
